What Are Macronutrients? Protein, Carbs, and Fats Explained
Confusion about nutrition starts with the basics. We break down exactly what protein, carbs, and fats do for your body and how to balance them for your goals.
Azeem Iqbal
Nutrition Expert

What Are Macronutrients? Protein, Carbs, and Fats Explained
If you have ever tried to get in shape, you have heard the word “Macros.”
“Does it fit your macros?” “I’m tracking my macros.” “You need to hit your protein macro.”
It sounds complicated, like advanced calculus for food. But it is actually very simple. Macronutrients (or “macros”) are just the three categories of nutrients that provide you with energy.
Think of your body like a construction site.
- Calories are the electricity keeping the lights on.
- Macronutrients are the raw materials: bricks, wood, and mortar. If you only care about electricity (calories), you might have power, but your house could fall down because you didn’t have enough bricks (protein).
In this guide, we will strip away the confusion and explain exactly what Protein, Carbs, and Fats do, and how to balance them for your goals.
Need your personal numbers? Don’t do the math yourself. Use our free Macro Calculator to find your perfect ratio instantly.

1. Protein: The Builder
Caloric Value: 4 Calories per gram.
Protein is the rockstar of the fitness world, and for good reason. It is the building block of life. Every cell in your body from your bicep muscles to your hair, skin, and enzymes is made of protein.
What It Does:
- Builds and Repairs Muscle: You tear muscle fibers in the gym; protein fuses them back together to be stronger.
- Keeps You Full: Protein is the most satiating nutrient. Eating a chicken breast keeps you full much longer than a bagel, even if the calories are the same.
- Boosts Metabolism: Your body burns more energy digesting protein than any other food.
Best Sources:
- Chicken breast, turkey, lean beef.
- Fish (Salmon, Tuna, Tilapia).
- Eggs and Greek Yogurt.
- Plant-based: Tofu, lentils, tempeh, beans.
Recommendation: Aim for 0.7g to 1g of protein per pound of body weight. If you weigh 150lbs, eat ~150g of protein.
2. Carbohydrates: The Fuel
Caloric Value: 4 Calories per gram.
Carbs have been demonized for years, but they are not the enemy. They are your body’s preferred source of gasoline. When you eat carbs, your body breaks them down into glucose (sugar), which powers your brain and muscles during high-intensity activity.
The Two Types:
- Complex Carbs (The Good): These come with fiber. They digest slowly and provide steady energy.
- Examples: Oats, brown rice, sweet potatoes, quinoa, vegetables, whole fruits.
- Simple Carbs (The “Fun”): These are stripped of fiber. They spike your blood sugar quickly and crash it just as fast.
- Examples: White bread, soda, candy, pastries, fruit juice.
Recommendation: Don’t fear carbs, but earn them. If you are sedentary, you need fewer. If you are an athlete, you need more. Focus 80% of your intake on complex sources.

3. Fats: The Protector
Caloric Value: 9 Calories per gram.
For decades, we were told “eating fat makes you fat.” This was a lie. Dietary fat is essential for your survival. It does not make you fat unless you eat too many total calories. In fact, cutting fat too low can destroy your health.
What It Does:
- Hormone Regulation: Your body needs fat to produce testosterone, estrogen, and other vital hormones.
- Brain Health: Your brain is roughly 60% fat.
- Vitamin Absorption: You cannot absorb Vitamins A, D, E, or K without fat.
The Types:
- Unsaturated (Healthy): Olive oil, avocados, nuts, salmon.
- Saturated (Neutral/Limit): Butter, coconut oil, fatty red meat.
- Trans Fats (Toxic): Artificial fats found in cheap processed snacks. Avoid these completely.
Recommendation: Never drop your fat intake below 15-20% of your total calories, or your hormones will suffer.
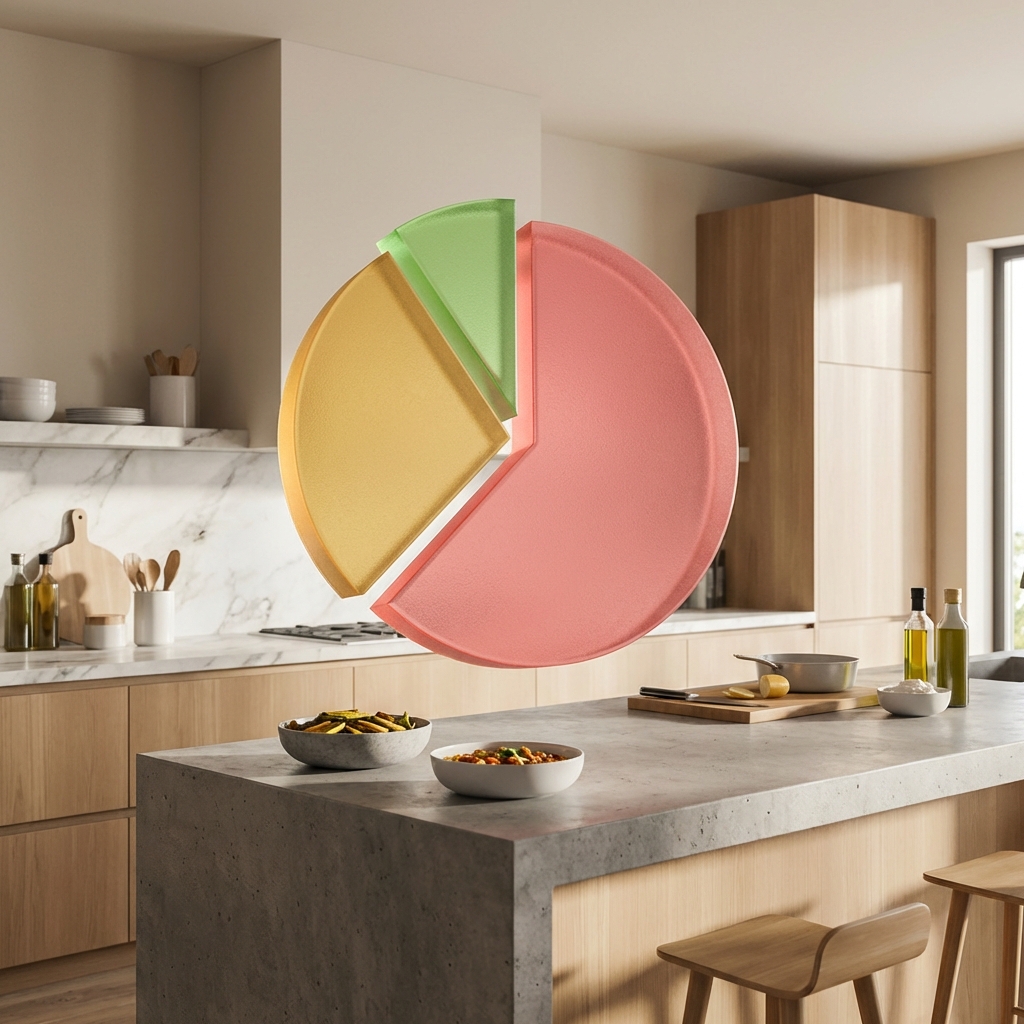
How to Balance Them (The Ratios)
So, how do you combine them? It depends on your goal.
1. The Balanced Diet (Maintenance / Beginners)
- 40% Carbs | 30% Protein | 30% Fats
- This is the “Zone” approach. It gives you enough energy for workouts, enough protein for recovery, and healthy fats for hormones.
2. The Low-Carb / Fat Loss (Endomorphs)
- 25% Carbs | 40% Protein | 35% Fats
- By lowering carbs, you control insulin levels and focus the body on burning fat. The high protein protects your muscle while you lose weight.
3. The Muscle Gain (Ectomorphs / Athletes)
- 50% Carbs | 30% Protein | 20% Fats
- To build size, you need energy. High carbs spare your protein so it can be used entirely for muscle building rather than energy.
Why “If It Fits Your Macros” (IIFYM) Works
The beauty of tracking macros is flexibility. The old way of dieting was rigid: “Chicken and broccoli only.” The Macro way is flexible: “I need 30g of carbs. I can have a sweet potato OR I can have a small serving of ice cream.”
As long as you hit your protein target and stay within your calorie limit, you can enjoy your favorite foods in moderation without ruining your progress. This is why people who track macros stick to their diets longer because they don’t feel deprived.
Summary
Nutrition isn’t magic. It’s just chemistry.
- Protein builds you.
- Carbs move you.
- Fats protect you.
Stop guessing portions and start understanding the numbers. Ready to find your perfect ratio? Click here to use the Macro Calculator and get your personalized plan in less than 60 seconds.
? Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 3 main macronutrients?
Which macronutrient is best for weight loss?
Do I need to count macros or just calories?
Is alcohol a macronutrient?
What is a good macro ratio for beginners?
Are carbs bad for you?
About Azeem Iqbal
We are dedicated to providing accurate, easy-to-understand nutritional information for Moe's Southwest Grill fans. Our goal is to help you make informed dining choices without sacrificing flavor.



